

E.51 BCD DIVIDE - Divides two values
| Description | Instruction divides the contents of location Dd with contents of location Dr. The result of division is stored in locations R and R+1. The first contains the rounded off result of division, while R+1 contains the fraction. |
| Ladder symbol | 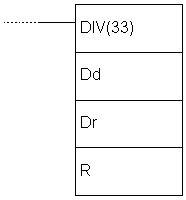 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if the contents of words Dd and Dr are not BCD. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. |
| Example |  Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction divides the value of memory location IR216 by the value of memory location HR09. The result is stored into two sequential memory locations DM0017 and DDM0018. The result is stored so that DM0017 contains round number and DM0018 contains the fraction. Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction divides the value of memory location IR216 by the value of memory location HR09. The result is stored into two sequential memory locations DM0017 and DDM0018. The result is stored so that DM0017 contains round number and DM0018 contains the fraction. |
E.52 DOUBLE BCD ADD - Adds two 32-bit words
| Description | Instruction adds values from addresses Au and Au+1 to values from addresses Ad, Ad+1 and carry bit CY. If the result exceeds 99999999 carry bit CY is set.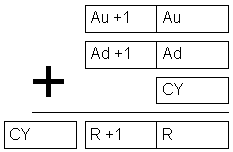 |
| Ladder symbol | 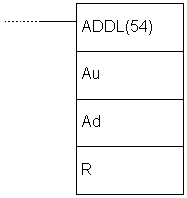 |
| Limitations | Word DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if the contents of words Au and Ad are not BCD. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. CY flag changes state to ON if there is a carry in the result. |
E.53 DOUBLE BCD SUBTRACT - Subtracts two 32-bit words
| Description | Instruction subtracts the contents of two words Su+1 and Su with carry bit CY added from the contents of words Mi+1 and Mi. The result is stored into memory locations R+1 and R. If the result is negative, carry bit CY is set and 10’complement of the result is stored into R. To get the real result, contents of R should be subtracted from zero.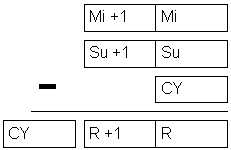 |
| Ladder symbol | 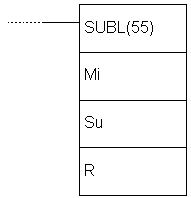 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if the contents of words Mi, Mi+1, Su, Su+1 are not BCD. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. CY flag changes state to ON if the result is negative. |
E.54 DOUBLE BCD MULTIPLY - Multiplies two pairs of words
| Description | Instruction multiplies values of locations Md, Md+1 with the values of locations Mr, Mr+1. The result is stored into 4 locations: R, R+1, R+2 i R+3.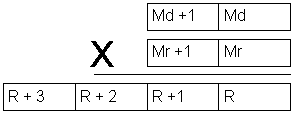 |
| Ladder symbol | 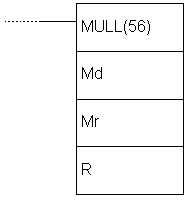 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if the contents of words Mr, Mr+1, Md and Md+1 are not BCD. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. CY flag changes state to ON if there is a carry in the result. |
E.55 DOUBLE BCD DIVIDE - Divides two pairs of words
| Description | Instruction divides the contents of locations Dd, Dd+1 by the contents of locations Dr i Dr+1. The result is stored into locations R and R+1 while locations R+2 and R+3 contain the fraction.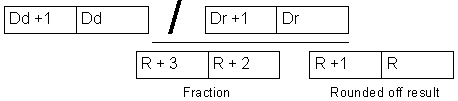 |
| Ladder symbol | 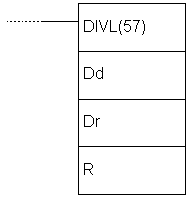 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in two cases, if the contents of words Dd, Dd+1, Dr and Dr+1 are not BCD or if the contents of locations Dr and Dr+1 equal zero. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. |
E.56 BINARY ADD - Binary addition
| Description | Instruction executes binary addition of words Au and Ad with carry bit and stores the result into memory location R. If the result is greater than FFFF the carry bit CY is set. | |
| Ladder symbol |  |
|
| Limitations | Words DM 6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. | |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. CY flag changes state to ON if the result is greater FFFF. OF flag changes state if the result is greater than +32.767 (7FFF). UF flag changes state if the result is lower than od +32.768 (7FFF). | |
| Example |  |
The example demonstrates how the binary addition works. As A6E2+80C5 equals 127A7, carry bit CY is set and the value of location R+1 (which is, in this case, on HR11) changes to “1” to enable easier handling of the result on addresses R and R+1 later in the program. If overflow occurs, carry bit CY will be set, fulfilling the condition on bit SR255.04. This condition controls the lower MOV instruction, which sets “1” to location HR11. |
 |
||
E.57 BINARY SUBTRACT - Binary subtraction
| Description | Instruction subtracts values Su+CY from the value Mi and stores the result into location R. If the result is negative, carry bit CY is set and the 2’complement of the real result is stored into location R. | |
| Ladder symbol |  |
|
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. | |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. CY flag changes state to ON if the result is negative. OF flag changes state if the result is greater than +32.767 (7FFF) UF flag changes state if the result is lower than +32.768 (7FFF). | |
| Example |  |
The example subtracts the value of location LR00 increased by the state of carry bit CY from the value of location IR200. As the result is positive, carry bit CY will not be set. In case of negative result, location HR01 would contain 2’complement of the result, so that a conversion would be necessary for getting the real result. |
 |
||
E.58 BINARY MULTIPLY - Binary multiplication
| Description | Instruction multiplies values of location Md by the value of location Mr. The result is stored in two memory locations R and R+1. |
| Ladder symbol | 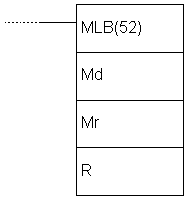 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state u ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state u ON if the result equals “0”. |
E.59 BINARY DIVIDE - Binary division
| Description | Instruction divides the value of location Dd with the value of location Dr. The result is stored into location R, while the fraction is stored in R+1.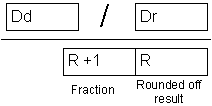 |
| Ladder symbol | 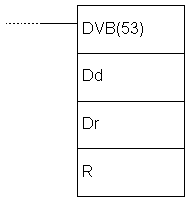 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R and the instruction cannot be used for dividing signed numbers. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case that Dr contains value “0”. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. |
E.60 BCD TO BINARY - Converts decimal number to a binary number
| Description | Instruction converts binary representation of decimal number from the word S to binary number in the word R. Contents of the word S remains unchanged. |
| Ladder symbol | 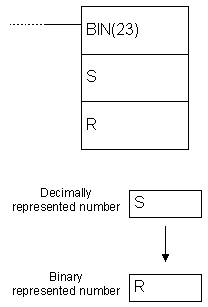 |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if the contents of the word S are not BCD. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. |
| Example |  Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction changes the contents of memory location IR200 so that its numerical value remains unchanged; in other words, only the representation of the location’s contents changes. If the contents of the location IR200 is “164” decimal, this instruction would convert it to “0000000010100100”. One of the purposes of this instruction is preparing the contents of memory location for one of the binary operations. Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction changes the contents of memory location IR200 so that its numerical value remains unchanged; in other words, only the representation of the location’s contents changes. If the contents of the location IR200 is “164” decimal, this instruction would convert it to “0000000010100100”. One of the purposes of this instruction is preparing the contents of memory location for one of the binary operations. |
E.61 BINARY TO BCD - Converts binary number to a decimal number
| Description | Instruction converts binary represented number from the word S to a decimal number in the word R. Contents of the word S remains unchanged. |
| Ladder symbol | 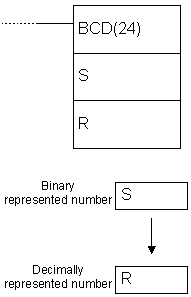 |
| Limitations | Word DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals “0”. |
| Example |  Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction changes the contents of memory location IR200 so that its numerical value remains unchanged; in other words, only the representation of the location’s contents changes. If the contents of location IR200 is “000000101100100” binarny, this instruction would convert it to “740” decimaly. One of the purposes of this instruction is preparing the contents of memory location for one of BCD operations. Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction changes the contents of memory location IR200 so that its numerical value remains unchanged; in other words, only the representation of the location’s contents changes. If the contents of location IR200 is “000000101100100” binarny, this instruction would convert it to “740” decimaly. One of the purposes of this instruction is preparing the contents of memory location for one of BCD operations. |
E.62 4 TO 16 DECODER - 4 to 16 decoder
| Description | Instruction converts up to four 4-bit hexadecimal digits of values from 0 to 15. The result of the instruction is stored into memory locations from address R to R+3, depending on how many digits was converted. Converted digit in the result is represented with a set bit on a position corresponding to the value of a digit. If the value of a digit is “C” (12 decimaly) the twelfth bit of the result word will be set.
 Some of the combinations of control word values along with their meaning are given below: Some of the combinations of control word values along with their meaning are given below:
|
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Two rightmost digits of the word Di have to be between 0 and 3. Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case that (R + number of digits) exceeds the range of a given memory block. |
| Example |  Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction converts three digits from the digit no.1 in the word DM0020. As there are three digits to be converted, the result will take three memory locations starting from HR10. Digit 0 in the word DM0020 is not converted. Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, instruction converts three digits from the digit no.1 in the word DM0020. As there are three digits to be converted, the result will take three memory locations starting from HR10. Digit 0 in the word DM0020 is not converted. |
E.63 16 TO 4 ENCODER - 16 to 4 encoder
| Description | Instruction determines the highest set bit in SB and according to it, stores the 4-bit hexadecimal value to a certain place in the result word R. In the example below, bit 12 of the location on address SB is set, which would be “C” in a hexadecimal representation.
Precise place for storing the converted value in the word R is determined by a control word Di. The same word also determines the number of words to be converted, starting from the address of the word SB. For this example, the control word would be “0001”.
The first digit to be converted, as well as the number of digits to be converted, is determined in the control word Di. If the number of digits for conversion is greater than the number of digits remaining in the word S, then the missing digits are taken from the starting digit anew. The structure of the control word Di is shown on the picture above. Some of the combinations of control word values along with their meaning are given below:
|
| Ladder symbol | 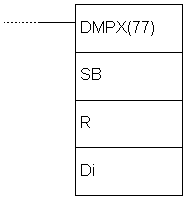 |
| Limitations | Two rightmost digits of the word Di have to be between 0 and 3. Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operands R, SB and Di. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if (SB + number of digits) exceeds the range of a given memory block or if the word to be converted equals zero. |
| Example |  Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, first DMPX instruction converts two words, IR200 and IR201. The control word is “0010”, meaning that two words are converted (digit 1) and stored starting from the zero digit in the result (rightmost digit 0). After the first DMPX instruction, the second one is executed, converting two words from addresses LR10 and LR11 and storing them in the result word HR10, starting from the digit no.2. Therefore, the word HR10 contains four converted words in the following order: IR200, IR201, LR10, LR11. More detailed explanation of how the instruction works is given on the following picture. Upon fulfilling the condition on bit IR000.00, first DMPX instruction converts two words, IR200 and IR201. The control word is “0010”, meaning that two words are converted (digit 1) and stored starting from the zero digit in the result (rightmost digit 0). After the first DMPX instruction, the second one is executed, converting two words from addresses LR10 and LR11 and storing them in the result word HR10, starting from the digit no.2. Therefore, the word HR10 contains four converted words in the following order: IR200, IR201, LR10, LR11. More detailed explanation of how the instruction works is given on the following picture.
|
E.64 ASCII CONVERT - Converts to ASCII code
| Description | Instruction converts digits from the word S to their ASCII equivalent and stores the result in the words starting from the address D. The control word Di determines the first converted digit, the number of digits to be converted and which half of the word D contains the first 8-bit ASCII converted code. IIf the number of digits for conversion is greater than the number of digits remaining in the word S, then the missing digits are taken from the starting digit anew from the word S. Digit with the highest position of the word Di has a role of parity bit and it can take values between 0 and 2 - not having parity, parity and non-parity. Parity bit is actually a highest bit of the 8-bit ASCII code. When the third digit of the word Di equals zero, this bit is always zero. If the third digit of the word Di equals one, then this bit represents parity, or simply put, this bit is set when the number of ones in the other 7 bits of ASCII is odd making the number of ones even. If the ASCII value equals “31” (binary “0011 0001”), even parity would change the highest bit to one, changing the ASCII number to “1011 0001” or “B1”. The status of parity bit does not affect the interpretation of ASCII code. Odd parity bit behaves in similar fashion, but with the opposite function. It’s purpose is to ensure that the number of ones in ASCII code is always odd. The following picture represents interpreting the value of word Di and the picture after that gives several versions of values of the word Di and how they affect the instruction.
|
| Ladder symbol | 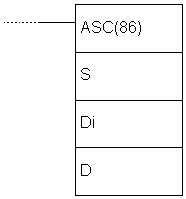 |
| Limitations | Two lower digits of the words Di must have values betweenmoraju imati 0 and 3. Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand D. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if two rightmost digits of the word Di do not fall within the specified range (0-3) or the result word exceeds the boundaries of memory area. |
E.65 COMPLEMENT - Complements a word
| Description | Instruction executes the second complement of the word Wd and stores it into word Wd again. The second complement means that ones become zeros and vice versa.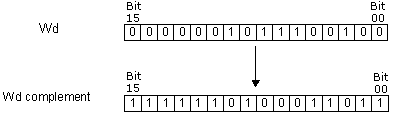 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand Wd. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.66 LOGICAL AND - Operation logical "AND" on the contents of a word
| Description | Instruction executes the operation logical “AND” on words I1 and I2. The result of the operation is stored into word R. Operation logical “AND” puts one in the result only if the same position of words I1 and I2 also contain one.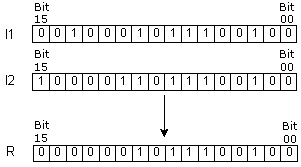 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM 6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.67 LOGICAL OR - Operation logical "OR" on the contents of a word
| Description | Instruction executes the operation logical “OR” on words I1 and I2. The result of the operation is stored into the word R. Operation logical “OR” puts the one in the result if at least one of the words I1 and I2 contains one on that position.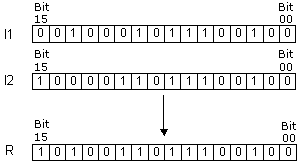 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.68 EXCLUSIVE OR - Operation "EXCLUSIVE OR" on the contents of a word
| Description | Instruction executes operation “EXCLUSIVE OR” on the words I1 and I2. The result of the operation is stored into the word R. Operation exlusive “OR” puts one in the result only if the same position of the words I1 and I2 contains different values.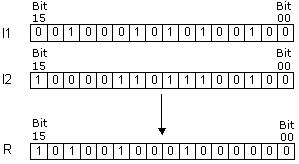 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.69 EXCLUSIVE NOR - Operation "EXCLUSIVE NOR" on the contents of a word
| Description | Instruction executes operation “EXCLUSIVE OR” on the words I1 and I2. The result of the operation is stored into the word R. Operation exclusive “NOR” puts one in the result only if the same position of words I1 and I2 contains the same value, whether it is “0” or”1”.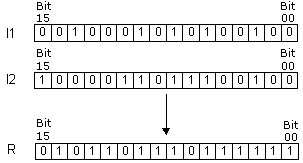 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.70 BIT COUNTER - Counts the number of ones in a given word
| Description | Instruction counts the number of bits with the state “1” in words from address SB to SB+(N-1) and puts the result on the address of the word R.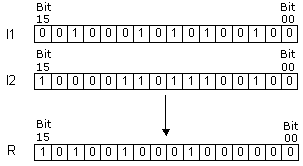 |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand R. Word N cannot have zero value. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case that N isn’t BCD number or in case that SB and SB+(N-1) don’t belong to the same memory area. EQ flag changes state to ON if the result equals zero. |
E.71 SUBROUTINE ENTRY - Enters the subroutine
| Description | Instruction changes the course of the main program towards subroutine, at the instruction line of the main program which contains the instruction SBS. Number of instructions N has to be in 000 - 049 range. When the instruction condition is fulfilled, all the instructions between SBN(92) and the first RET(92) instruction are executed. Upon processing the RET instruction, program returns to the line immediately following the instruction SBS which called the subroutine in the first place. The same subroutine may be called from several places in the program.
|
| Ladder symbol | 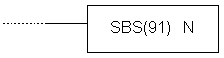 |
| Limitations | Number of subroutine has to be in 000 - 049 range. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON when non-existing subroutine is called, when the subroutine calls itself or when the subroutine being executed at the moment is called. |
E.72 SUBROUTINE DEFINE - Beginning of a subroutine
| Description | Instruction marks the beginning of a subroutine. Each subroutine is defined with its number N. All subroutines have to be placed after the main program and instruction END has to follow the last RET instruction of the last subroutine SBN.
|
| Ladder symbol | 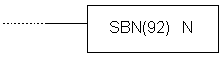 |
| Limitations | Number of the subroutine has to be in 000 - 049 range. Each number may be used only once. |
| Flag | It has no effect on any particular flag. |
E.73 SUBROUTINE RETURN - Return from a subroutine
| Description | Instruction executes the return from the subroutine to the main program. Each subroutine must contain the RET instruction. This instruction jas on number of its own, naturally assuming that it belongs to the previous SBN instruction.
|
| Ladder symbol | 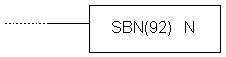 |
| Limitations | Number of the subroutine has to be in 000 - 049 range. Each number may be used only once. |
| Flag | It has no effect on any particular flag. |
E.74 MACRO - Macro
| Description | Instruction MCRO enables one subroutine to substitiute several subroutines having the same structure, but different operands. Instruction has 4 input words SR232 to SR235 and 4 output words SR236 to SR239 used for sending or receiving the subroutine parameters. Upon fulfilling the condition, the instruction copies the contents of locations I1 - I3 to words SR232 - SR235. Upon execution of subroutine N, values of the words SR236 - SR239 are copied to words O1 - O3. |
| Ladder symbol | 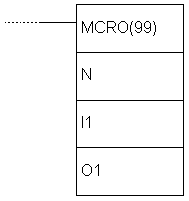 |
| Limitations | Number of the subroutine has to be in 000 - 049 range. Each number may be used only once. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON when non-existing subroutine is called, when the subroutine calls itself or when the subroutine, being executed at the moment, is called. |
| Example |
|
E.75 INTERRUPT CONTROL - Interrupt control
| Description | Instruction controls the interrupts and executes one of the seven functions presented in the table below, according to the value of the word C1.
 C1=001 Function resets the registered interrupts, so that interrupt routine cannot take place upon unmasking the interrupt input. Bits 4, 5, 6...15 of the word C2 should be set to zero. C1=001 Function resets the registered interrupts, so that interrupt routine cannot take place upon unmasking the interrupt input. Bits 4, 5, 6...15 of the word C2 should be set to zero.
C1=002 Function reads the status of the mask for interrupt inputs 00003 - 00006 and stores the read state into the word C2. Interrupt input is masked if the state of the corresponding bit equals “1”. Bits 00 - 03 correspond to interrupt inputs 00003 - 00006.
C1=003 Function restarts the interrupt inputs in the counter mode. The current counter value (SR240 - SR243) is set to the starting state and the interrupt is unmasked. If C1=003, decremental counter is restarted, while in the case of C1=004 incremental counter is restarted. As CPM1A model of PLC does not feature incremental counter, this option should not be used. When using the options C1=003 or C1=004 differencial form of the instruction shoud be used @INT or else the current counter state (PV) will be reset to the starting state (SV) and the interrupt will never be generated. Writing the value “0000” to the starting counter state and executing the INT instruction with parameter C1=003 stops the counter and disables interrupts. To start the counter again, non-zero value should be written to a starting value SV and the instruction INT executed. Interrupts in the counter mode can be masked by executing the instruction INT with parameter C1=000 and set corresponding bit in C2. If same is done, but with “0” for the appropriate position in the word C2 interrupt input will behave as a regular interrupt ulaz and not as counter interrupt input.
C1=100 Function masks all the interrupts including the interval timer interrupts and the high-speed counter interrupts. Masked interrupts are registered, but are not executed. This function is also called a global interrupt mask and it does not affect the masks of specific interrupts. This option should be used for temporary disabling all the interrupts. It is cmmonly used in pair, one function masks all the interrupts and the other one unmasks them. Function cannot be used within the interrupt routine.
C1=200 Function unmasks all the interrupts including the interval timer interrupts and the high-speed counter interrupts. If the specific interrupt is masked, global unmasking does not affect the state of the specific interrupt input state. Function cannot be used within the interrupt routine.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Ladder symbol |  |
||||||||||||||||
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if: C1 is not 000, 001, 002, 003, 004, 100 or 200. C2 is not in 0000 - 000F range. INT instruction is executed with C1=100 or 200 within the interrupt routine. INT instruction is executed with C1=100 when all inputs are already masked. INT instruction is executed with C1=200 when all inputs are already unmasked. |
E.76 INTERVAL TIMER - Interval timer
| Description | Instruction is used for controling the timer interrupt. Instruction mode is determined according to the value of the word C1.
|
||||||||||
| Ladder symbol |  |
||||||||||
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if C1 is not 000, 003, 006 or 010 or in case that the number of interrupt routine is not within 0000 - 0049 range. |
E.77 7-SEGMENT DECODER - Seven-segment decoder
| Description | Instruction translates the digits of the word S to 8-bit 7-segment code and stores it into destination word D. The control word Di determines the first digit of S to be translated, number of digits to be translated and which half of the word D will contain the result of the first translation. The following picture interprets the values of digits of the word Di and the picture after that displays a few versions of the word Di and how they affect the instruction. |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand D. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. |
| Example |  |
E.78 I/O REFRESH - Premature writing to I/O table
| Description | Instruction checks the states of words from the address St to the address E and refreshes them according to the current state of the program. Instruction is used when we want to know the state of certain bit without waiting it to be refreshed in the course of regular cycle of refreshing the inputs and outputs of PLC controller (IR000 - IR019). |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Address of the word St has to be lower or equal to the address of the word E. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if words St and E do not belong to IR000 - IR019 range or in case that the address of the word St is greater than the address of the word E. |
E.79 MESSAGE - Displays message in the programming console
| Description | Instruction reads the contents of eight words from the address FM and displays them in the program console. Contents of the word has to be in ASCII format, with every word containing 2 ASCII characters. If not all the words are to be displayed in the console, displaying can be stopped if the string “OD” is put into following word. |
| Ladder symbol |  |
| Limitations | Words DM6144 - DM6655 cannot be used as operand FM. |
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON in case of error. |
E.80 MODE CONTROL - Controls the high-speed counter or the pulse output
| Description | Instruction controls the high-speed counter. There are several functions depending on parameters P, C and P1. Parameter P defines if either high-speed counter or pulse output will be controlled with this instruction.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ladder symbol | 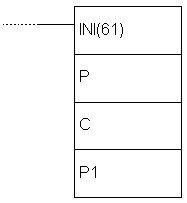 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limitations | If CPM1 or CPM1A PLC controller is used, parameter P has to be 000 and parameter C has to be 000, 001, 002 or 003. P1 has to be 000 if C is not 002 or 004. If an address from DM memory area is used as parameter P1, reading and writing to that location has to be enabled. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if comparison table exceeds one memory area. |
E.81 HIGH-SPEED COUNTER PV READ - Reads the current value of high-speed counter
| Description | Instruction controls the current state of high-speed counter, pulse output, interrupt input in counter mode or input frequency for synchronized input. There are several functions depending on parameters P, C and D.Parameter P defines if either high-speed counter or pulse output will be controlled with this instruction.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ladder symbol | 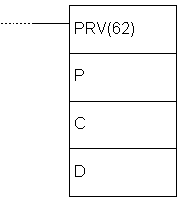 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limitations | If CPM1 or CPM1A PLC controller is used, parameter D has to be 000 and parameter C has to be 000, 001 or 002. If an address from DM memory area is used as parameter D, reading and writing to that location has to be enabled. D and D+1 have to belong to the same memory area. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if an error concerning the value of instruction operand occurred. |
E.82 COMPARISON TABLE LOAD - Defines a comparison table
| Description | Instruction forms the comparison table for working with high-speed counter. Depending on parameter C, comparison can be immediate or it can be called upon with instruction INI.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ladder symbol | 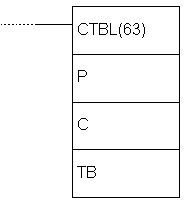 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Limitations | In each area lower border has to be lower than the upper border. Number of subroutine can be used for several ranges. Table has to belong to a single memory area. Parameter D has to be 000 and the parameter C has to be 000, 001, 002 or 003. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flag | ER flag changes state to ON if an error concerning the value of instruction operand occurred. |
E.83 FAILURE ALARM AND RESET - Generates error code
| Description | Instruction generates the code of an error that took place, so that the programmer can use that information for debugging or program maintenance. Error code is stored in the first 8 bits of the word SR253 and has value between 01 and 99.
|
| Ladder symbol | 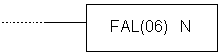 |
E.84 SEVERE FAILURE ALARM - Generates fatal error code
| Description | Instruction generates the code of an error that took place, so that the programmer can use that information for debugging or program maintenance. Error code is stored in the first 8 bits of the word SR253 and has value between 01 and 99. Upon occurence of fatal error, diode ALARM/ERROR turns on on the casing of PLC controller and the PLC stops operating.
|
| Ladder symbol |  |
E.85 SET CARRY - Sets carry bit
| Description | Instruction changes the state of carry bit CY to ON. Carry bit is an integral part of the word SR255, and its address is SR255.04. |
| Ladder symbol |  |
E.86 CLEAR CARRY - Resets carry bit
| Description | Instruction changes state of carry bit CY to OFF. Carry bit is an integral part of the word SR255, and its address is SR255.04. |
| Ladder symbol |  |